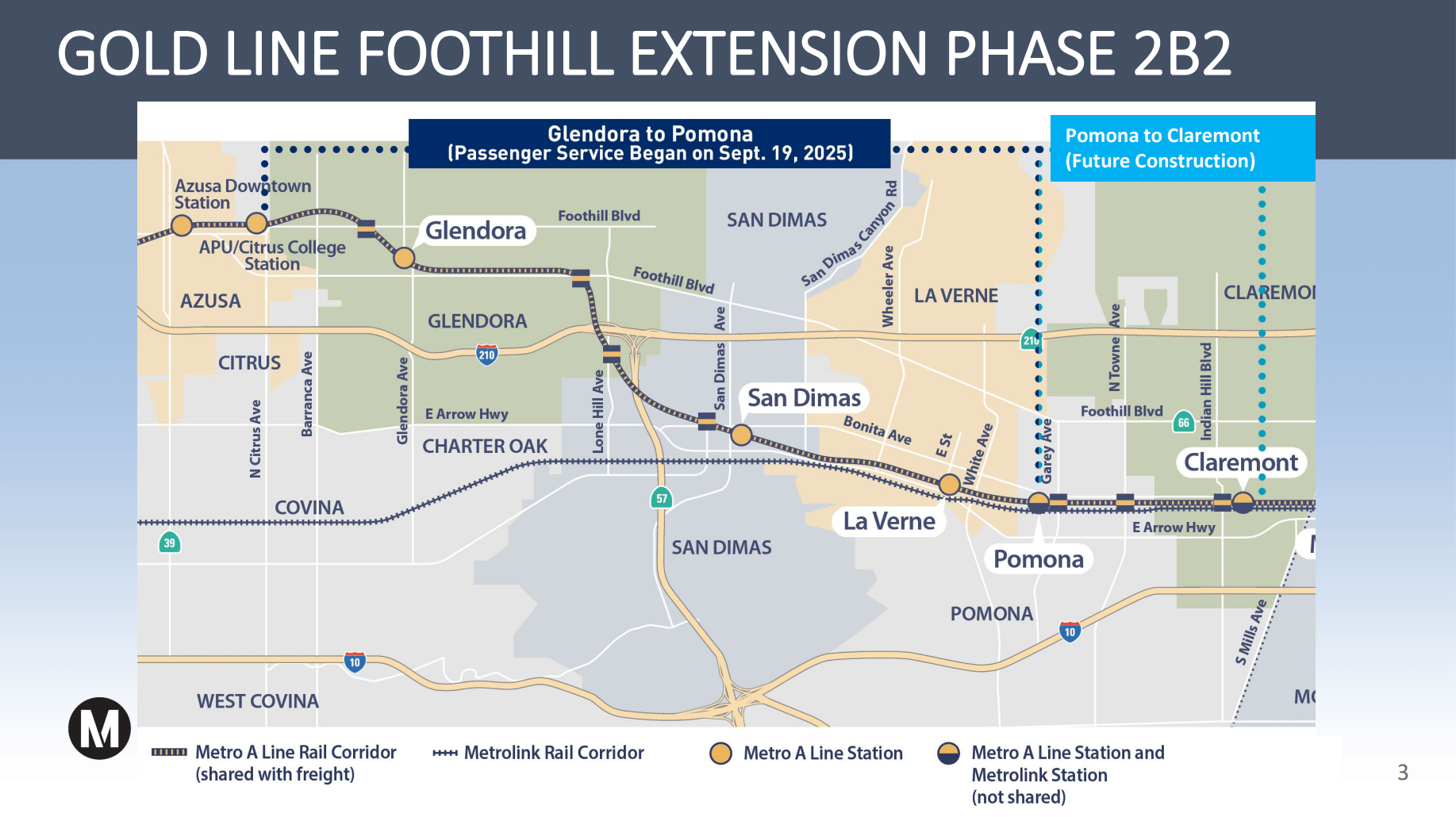
At some point over the past few years, a lot of my friends started moving to Silver Spring and Takoma Park and Falls Church. These inner-ring, transit-connected suburbs of DC are still far less compact and walkable than the neighborhoods my friends moved from. So they bought cars.
Why did they do this? They're entering peak driving age, which is historically between 35 and 54. They have more money than they did in their early 20s. But mostly, they had kids. Of all my friends, I now have exactly one that is still proudly car-free with kids.
In light of the new U.S. PIRG and Frontier Group report on changing driving habits, led by young people, we have to ask: Won’t those young people also drive more as they get older?
Reports of diminished interest in driving focus on two groups: baby boomers, the generation that came of age with the automobile and settled in car-dependent suburbs, who are now retiring and driving less; and millennials, the oldest of whom are 30 now and the youngest of whom aren’t even old enough to drive.
Millennials’ shift away from automobile travel is well documented, especially in last year’s report, "Transportation and the New Generation," by U.S. PIRG and the Frontier Group. That report found that between 2001 and 2009, annual driving by the 16-to-34 age cohort decreased 23 percent, from 10,300 miles to 7,900 miles per capita. That age group also took 24 percent more trips by bike and 40 percent more trips by public transit over those eight years.
With more and more people starting families later in life, the vast majority of millennials haven’t had babies yet. They also haven’t hit their prime earning years, which tend to be prime driving years.
That’s right, said Phineas Baxandall of U.S. PIRG, co-author of the transformative new report, "A New Direction," which outlines three possible scenarios for driving trends in the coming years, all of which would mean far less driving than government models predict.
“Our scenarios all assume that millenials will drive more when they get older,” Baxandall told Streetsblog. “The real question isn’t, ‘Will millennials drive more as they get older?’ It’s, ‘Will they drive more than their parents as they get older?’”
There are persuasive reasons to think they won’t.
First, what were the factors that led to what U.S. PIRG and Frontier Group call “the Driving Boom”? Massive highway expansion, bankrolled by a fat Highway Trust Fund. Suburban sprawl. The rise of the working woman. A 1950s car culture of cruising down the main drag, having burgers and milk-shakes in your car, even watching movies from your car.
Let's start with car culture. Young people now say that losing their computer or their cell phone would be a far greater loss than losing their car, if they even have one. Baby boomers still say losing their car would be the most disastrous. And millennials just haven't inherited that excitement over cars or the desire to spend their time tending to them. They don't see cars as a hobby, just a way to get around -- and an increasingly inconvenient one. According to the report, "less than 15 percent of millennials describe themselves as 'car enthusiasts' as opposed to 30 percent of baby boomers."
Meanwhile, we just can't sprawl much more. We’re running out of room to build new highways, and we’re running out of money faster. The Highway Trust Fund, as we’ve endlessly reported, is in serious crisis, expected to go bankrupt in 2015. And household economics prevent another major rush to buy cars: U.S. households had 1.24 vehicles per driver in 2006, a number which has dropped only slightly and is unlikely to rise again.
Sprawl is stalling for a variety of reasons, one of which is that people simply can’t tolerate much longer driving distances. Studies have shown that most people aren’t willing to spend more than 1.1 to 1.3 hours per day traveling, or roughly a half-hour commute each way to work. (There are exceptions to this general rule.)
The half-hour limit on commute times probably has some give. It stands to reason that a longer commute spent multi-tasking, as is possible on transit, would be more tolerable to many people. Biking and walking commutes can help people save time by skipping the gym. But it’s hard to see people suddenly happy to spend more time stuck in traffic.
And as Baxandall and co-author Tony Dutzik say in the report, driving speeds have probably peaked. “Barring major technological advances,” they write, “there are few prospects for a repeat of the quantum leap in travel speeds that occurred during the Driving Boom.”
Driverless vehicles are supposed to be the next "major technological advance," which would ostensibly allow for less congestion, increased safety, and higher speeds. But while driverless cars have already been tested, the full communications network that could really change the way the transportation system functions is a long way off. “We’re far enough off from those systems being viable that I think it shouldn’t be affecting our decisions about transportation investment right now,” Baxandall said.
Meanwhile, despite new forms of gasoline coming on the market, prices aren’t expected to drop. High gas prices have already changed the way people travel, encouraging people to choose transit over driving in record numbers. Those changes are likely to harden into long-term trends if gas prices stay high, causing people to “reorient their lives to avoid the expense of fuel,” the report says. One main way to avoid paying for gas is to avoid driving. That’s helped jump-start the return to the cities.
But it’s not just that young people are sick of traffic jams. They like cities. They like the vibrant sidewalk culture of a walkable town, the accessibility of a variety of amenities, and the short travel times – by a variety of modes – that are possible in the city. The growing preference for urban living is well documented, and the outer suburbs are losing popularity.
But the biggest change might be technology. We’ll explore all the ways that technology is changing travel habits in our next post.